How to implement a custom device#
Info
This guide is about how you can implement a custom device in Python. This allows you to develop your own device logic.
 1. Get the documentation#
1. Get the documentation#
Danger
The device documentation is essential for implementing your custom device. Please get an overview and keep the documentation ready during development.
 2. Lookup the interface#
2. Lookup the interface#
Abstract
To implement your custom device, you must know the device class of your custom device and open the corresponding documentation from Measmatic at GENERICDEVICE, e.g. SMU.
Tip
In the documentation you can see which methods are implemented in the device class in order to use or overwrite them. Please make sure to name your methods in the same way if you want to make an individual implementation.
 3. Create device class#
3. Create device class#
Example
Please open Visual Studio Code and create a Python file in the Measmatic/PythonDevices folder. First you have to instantiate a configuration. Set your device class there, e.g. SMU. Then instantiate a class that inherits from the device class and transfer the configuration into it.
from measmatic import CommunicatorType, Device, DeviceConfiguration
import uuid
# Configuration
class Keithley2400Config(DeviceConfiguration):
"""Configuration of the Keithley 2400 series SMU."""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
"SMU",
"Keithley 2400 series SMU",
CommunicatorType.GPIB | CommunicatorType.RS232
)
# Device
class Keithley2400(Device):
"""Keithley 2400 series SMU class."""
def __init__(self, d):
super().__init__(d)
self.device_configuration: Keithley2400Config
def initialize(self):
pass
 4. Select interpreter#
4. Select interpreter#
Tip
To view the supported methods and use autocompletion, you must load the Python interpreter from Measmatic into Visual Studio Code. Visual Studio Code > Select Interpreter > Select Interpreter Path // TODO: Show interpreter path
 5. Implement your device#
5. Implement your device#
Example
Now implement the code so that your device is implemented correctly. In this example, we use measure_iv as the entry point. The other methods follow this logic. This is what the sample implementation now looks like.
Tip
Don't forget to use the prepared methods, such as initialize, send_line, receive_line etc. as you can see in GENERICDEVICE. You can also throw an exception if unexpected behavior occurs. This is already supported in Measmatic.
from measmatic import CommunicatorType, Device, DeviceConfiguration
from enum import auto, Enum, Flag
import time
import uuid
class KeithleyModel(Enum):
Undefined = 0
Keithley2400 = 1
class Keithley2400Config(DeviceConfiguration):
"""Configuration of the Keithley 2400 series SMU."""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
"SMU",
"Keithley 2400 series SMU",
CommunicatorType.GPIB | CommunicatorType.RS232
)
self.guid = uuid.uuid4()
self.name = None
def create_device(self):
return Keithley2400(self)
class Keithley2400(Device):
"""Keithley 2400 series SMU class."""
class SenseFunc(Flag):
NONE = 0
VOLT = auto()
CURR = auto()
VOLT_CURR = VOLT | CURR
UNKNOWN = auto()
class SourceFunc(Enum):
VOLTAGE = 0
CURRENT = 1
class Output(Enum):
UNKNOWN = 0
ON = 1
OFF = 2
class Range(Enum):
UNKNOWN = 0
AUTO = 1
FIX = 2
def __init__(self, d):
super().__init__(d)
self.device_configuration: Keithley2400Config
self.model = KeithleyModel.Undefined
self._output = self.Output.UNKNOWN
self._sense_func = self.SenseFunc.UNKNOWN
self._range_curr = self.Range.UNKNOWN
self._source_function = None
self._voltage_bias = 0.0
self._current_compliance = 0.0
def initialize(self):
pass
def measure_iv(self) -> tuple[float, float]:
voltage, current = self.measure()
return current, voltage
def measure(self) -> tuple[float, float]:
if self._output != self.Output.ON:
raise Exception("Cannot measure with output off")
self.set_sense_func(self.SenseFunc.VOLT_CURR)
self.send_line("read?")
val_str = self.receive_line()
vals = val_str.split(",")
voltage = float(vals[0])
current = float(vals[1])
return voltage, current
def get_idn(self) -> str:
self.send_line("*IDN?")
return self.receive_line().strip()
def output_off(self):
if self._output != self.Output.OFF:
self.send_line("OUTP OFF")
self._output = self.Output.OFF
def output_on(self):
if self._output != self.Output.ON:
self.send_line("OUTP ON")
self._output = self.Output.ON
def set_sense_func(self, sense_func):
if self._sense_func != sense_func:
if sense_func == self.SenseFunc.VOLT_CURR:
self.send_line(":func:conc on")
self.send_line(":func 'volt','curr'")
elif sense_func == self.SenseFunc.VOLT:
self.send_line(":func:off:all")
self.send_line(":func:conc off")
self.send_line(":func 'volt'")
elif sense_func == self.SenseFunc.CURR:
self.send_line(":func:off:all")
self.send_line(":func:conc off")
self.send_line(":func 'curr'")
elif sense_func == self.SenseFunc.NONE:
self.send_line(":func:off:all")
else:
raise AssertionError("Unknown sense function")
self._sense_func = sense_func
def remote_sense(self, enable: bool):
self.send_line("syst:rsen on" if enable else "syst:rsen off")
def reset(self):
self.send_line(":ABOR")
self.send_line("*RST")
time.sleep(0.1)
self.clear_internal_state_vars()
idn = self.get_idn()
if "MODEL 2400" in idn:
self.model = KeithleyModel.Keithley2400
else:
raise Exception(f"Unsupported SMU model: {idn}")
self.send_line("SYST:CLE")
self.send_line("SYST:BEEP:STAT OFF")
self.send_line("SOUR:CLEAR:AUTO OFF")
self.send_line("SENS:FUNC:OFF:ALL")
self.send_line("form:elem volt,curr,time,stat")
def set_voltage(self, voltage, current_compliance):
self.check_voltage(voltage)
self.set_source_func(self.SourceFunc.VOLTAGE)
self.set_curr_compliance(current_compliance)
self.enable_auto_range_curr(True)
if self._voltage_bias != voltage:
self.send_line("sour:volt:mode fix")
self.send_line(f"sour:volt {voltage}")
self._voltage_bias = voltage
def set_source_func(self, source_function):
if self._source_function != source_function:
if source_function == self.SourceFunc.VOLTAGE:
self.send_line("SOUR:FUNC VOLT")
elif source_function == self.SourceFunc.CURRENT:
self.send_line("SOUR:FUNC CURR")
else:
raise AssertionError("Unknown source function")
self._source_function = source_function
self._output = self.Output.OFF
def set_curr_compliance(self, compl):
if compl == 0:
raise Exception(self, "Compliance must not be zero")
compl = abs(compl)
if self._current_compliance != compl:
if self._range_curr != self.Range.AUTO:
if self._current_compliance < 0:
self.send_line("sens:curr:prot?")
self._current_compliance = float(self.receive_line())
if compl > self._current_compliance:
self.send_line(f"sens:curr:prot {compl}")
self.send_line(f"sens:curr:rang {compl}")
else:
self.send_line(f"sens:curr:rang {compl}")
self.send_line(f"sens:curr:prot {compl}")
else:
self.send_line(f"sens:curr:prot {compl}")
self._current_compliance = compl
def enable_auto_range_curr(self, auto_range):
if auto_range:
if self._range_curr != self.Range.AUTO:
self.send_line("sens:curr:rang:auto on")
self._range_curr = self.Range.AUTO
else:
if self._range_curr != self.Range.FIX:
self.send_line("sens:curr:rang:auto off")
if self._current_compliance > 0:
self.send_line(f"sens:curr:prot {self._current_compliance}")
self.send_line(f"sens:curr:rang {self._current_compliance}")
self._range_curr = self.Range.FIX
def check_voltage(self, voltage):
if self.model == KeithleyModel.Keithley2400 and not (-200 <= voltage <= 200):
raise Exception(self, "Voltage out of Range (-200V <= voltage <= 200V)")
def clear_internal_state_vars(self):
self.model = KeithleyModel.Undefined
self._output = self.Output.UNKNOWN
self._sense_func = self.SenseFunc.UNKNOWN
self._range_curr = self.Range.UNKNOWN
self._source_function = self.SourceFunc.VOLTAGE
self._voltage_bias = -1000000.0
self._current_compliance = -1000000.0
 6. Setup your device#
6. Setup your device#
Info
Now connect your device, install any necessary drivers and configure the device as you need it.
 7. Initialize your device#
7. Initialize your device#
Tip
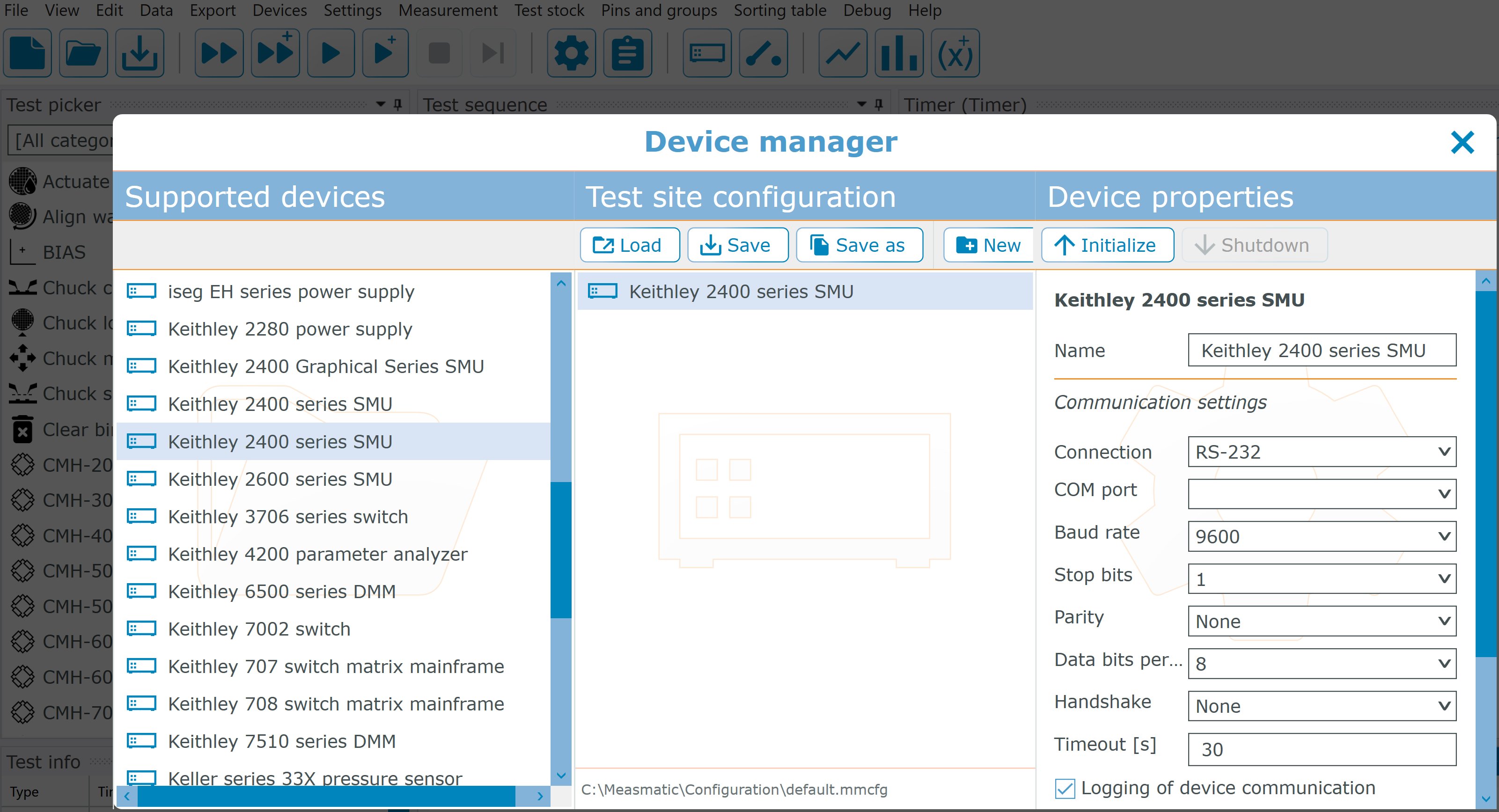
Now open the device manager in Measmatic. There you can select your device, mirror the configuration and initialize the device.

 8. Test your custom device#
8. Test your custom device#
Success
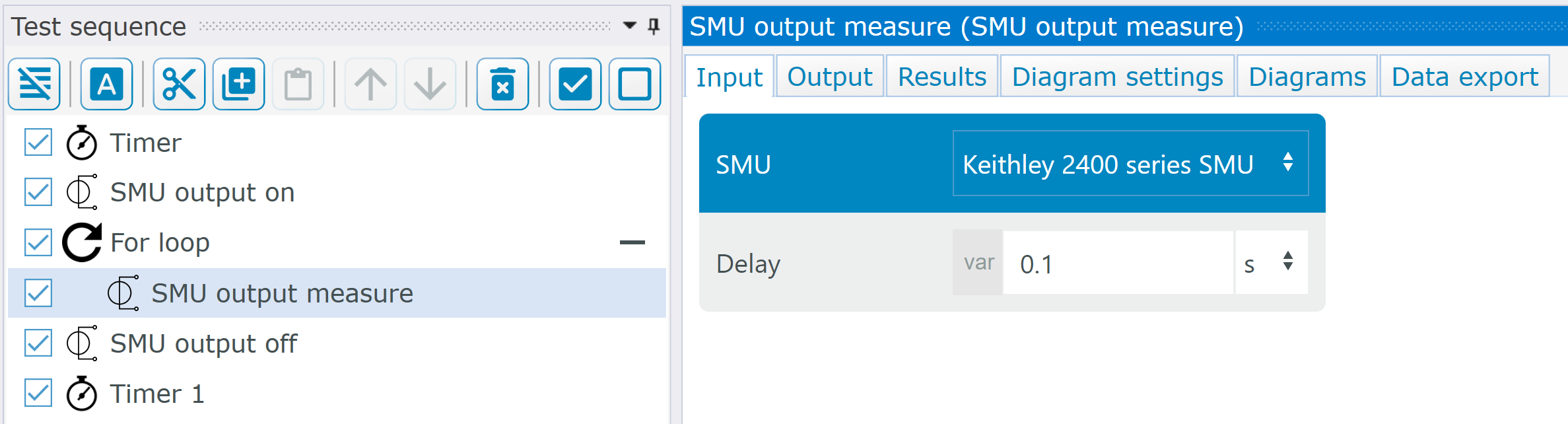
Now create a test sequence in a project that contains device that you have previously implemented in Python. Then execute the test sequence and check whether the application and the behavior work correctly.
 9. Test your device in a custom test#
9. Test your device in a custom test#
Success
Now create a new test and import your device.
import sys
dir_path = r"C:\Measmatic\PythonDevices"
if dir_path not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(dir_path)
from measmatic import TestInterface
from ...PythonDevices.keithley_2400 import Keithley2400 // ./../...
def Test(measmatic: TestInterface):
device: Keithley2400 = measmatic.get_device("Keithley2400")
device.initialize()